Business restructuring for
A $16 billion IT services multinational company was experiencing slowing revenue growth, decreasing profitability at 4%, declining asset utilization, and deteriorating stock value as it was operating below its cost of capital of 7%.
The company comprised 18 business segments and 12 service lines. The business segments were a mix of geographies, including the following:
– U.S.
- Manufacturing
- Transport
- Government
- Financial services
- Health
- Energy
- Communications
– Non-U.S. Americas
– EMEA
- U.K.
- Benelux
- France
- Germany
- Iberia
- Italy
- Nordic
- Switzerland
- Middle East
– Asia Pacific
- Australia
- Japan
The service lines included the following:
- Enterprise applications
- Systems development
- Systems integration
- Systems improvement
- Centralized system management
- Distributed system management
- Communications management
- Enterprise customer management
- Functional business process outsourcing
- IT consulting
- E-business
- Transaction processing
The company was getting disrupted across most markets and most service lines, without apparent countermeasures to put in place.
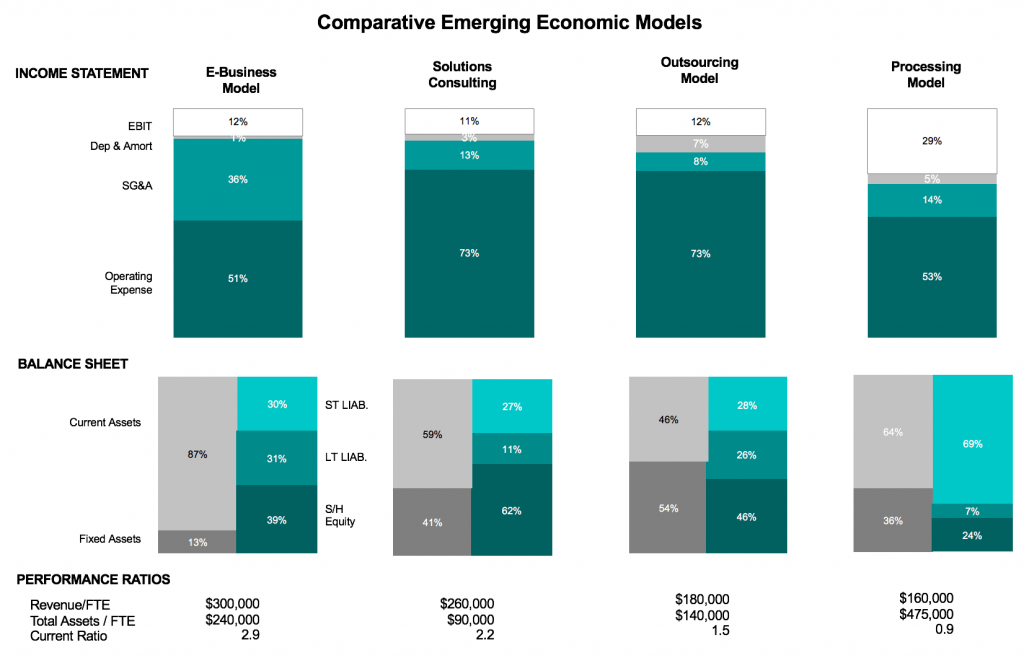
• Restructured the business into four lines of business grouped by service line, including
- Processing
- Outsourcing
- Solutions Consulting
- E-business
• Exited Payroll Processing, Financial Processing, and Technical products through sale
• Deployed business units for growth, including
- dedicating resources to Outsourcing for greater market penetration
- improving Solutions Consulting’s weak position (ERP Implementation, Application Development, IT Consulting, Process Consulting) through a flagship acquisition and niche acquisitions to close capability gap
- exploiting fast-growing E-Business opportunities
- consolidating Claims Processing through acquisition
• Redeployed internal resources to develop higher value services, canceling other initiatives
• The net effect was to
- stabilize the company
- reposition the business units for growth in attractive markets
- reverse profit deterioration in the first year
- cut revenue by $450 million
- increase contribution by $60 million
- reduce operating assets by $585 million
- improve asset utilization to 1.7x
- exceed the cost of capital
- Identified strategic industry trends, including
• structural constraints due to labor shortage
• increased value-added offerings through bundling, pricing models, branding, and broad service offerings
• specialization by service x customer type
• standardization of “formula” facilities to serve divers market needs
• acquisitions for critical mass - Measured market size and future growth by service line
- Estimated market share of company and leading competitors by service line
- Conducted an in-depth analysis of the competition, axes of profitability, direct competitors, financial strength, and strategic direction of each
- Identified four emerging economic models defined by
• operating expenses
• deployment of operating assets
• financial performance measures, and
• competitive strategy - Mapped the existing 12 service lines against the four emerging economic models, including
• Processing
• Outsourcing
• Solutions Consulting
• E-business - Developed the strategic direction and financial valuation for each, including grow, maintain, harvest, exit
- Drew a summary plan with the CFO and quantified financial value