Great Prairie Group follows the performance of the U.S. economy and publishes a quarterly overview with a dashboard of indicators and implications for business.
THE U.S. ECONOMY: A DASHBOARD
Q2 2019 marks a period of continued economic uncertainty, fueled by mixed economic results and political instability.
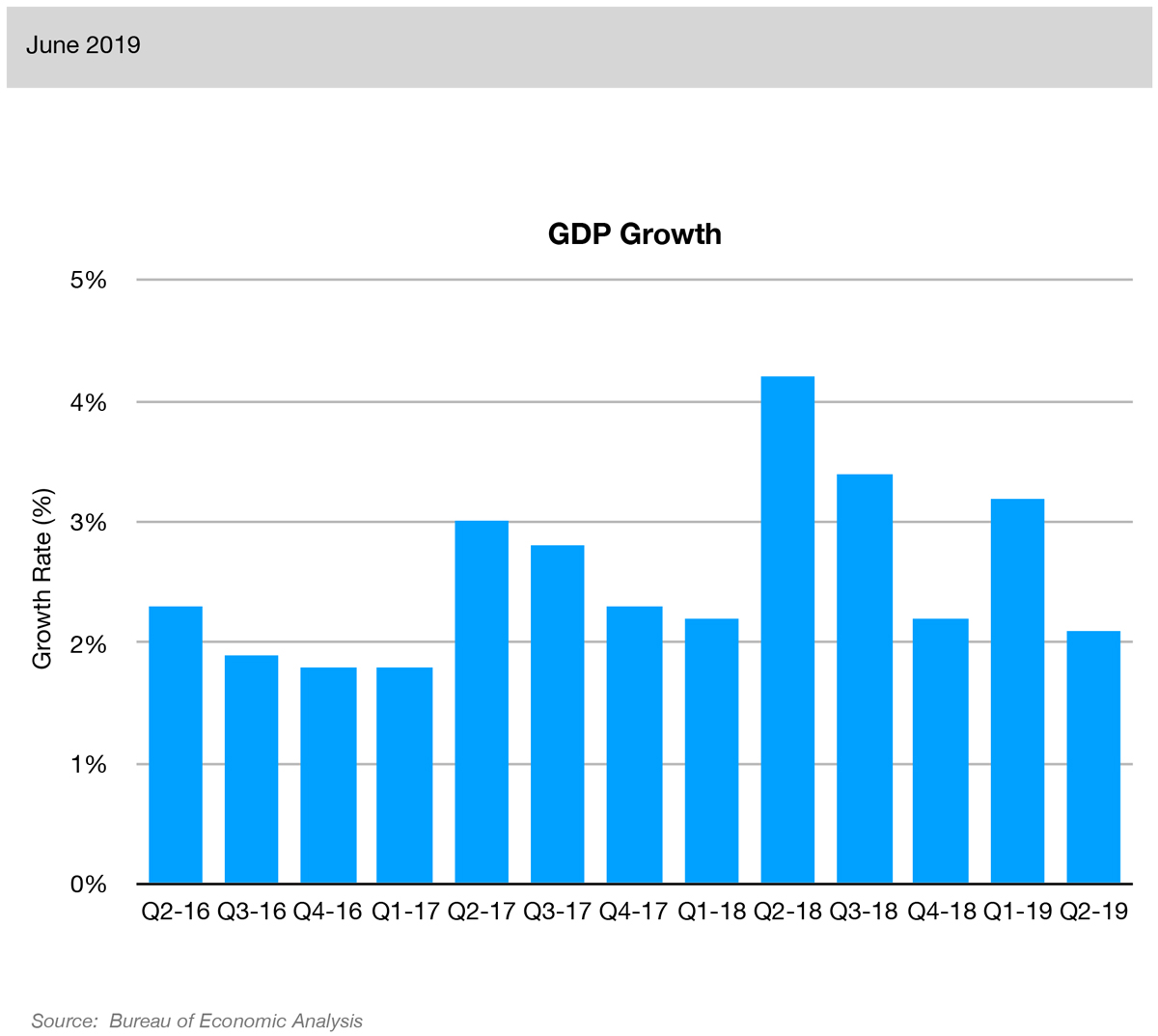
“Advance” GDP Growth for the quarter posted a rate of 2.1%, slowing down from GDP growth of 3.2% in the previous quarter. This slowdown is not surprising given that Q1 GDP growth was driven by an increase in inventories and a decrease in imports, two volatile components that provided a short-term boost.
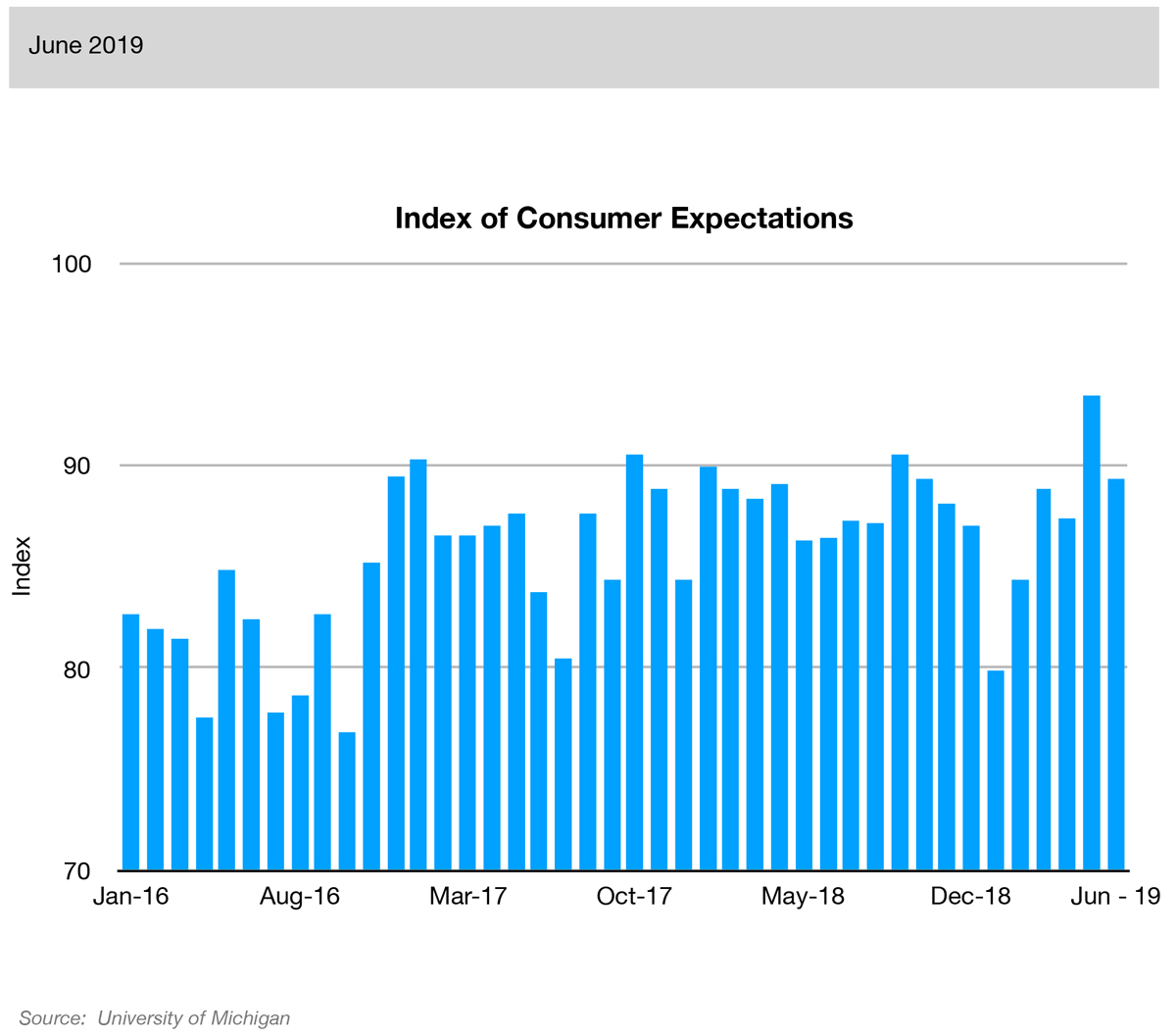
The bigger picture that has been playing out is that two different sides of the U.S. economy appear to be sending conflicting messages. On the one hand, U.S. consumers continue to buy goods (Advance Retail Sales at 1.3%) and show positive expectations about the future (Index of Consumer Expectations at 0.6%).
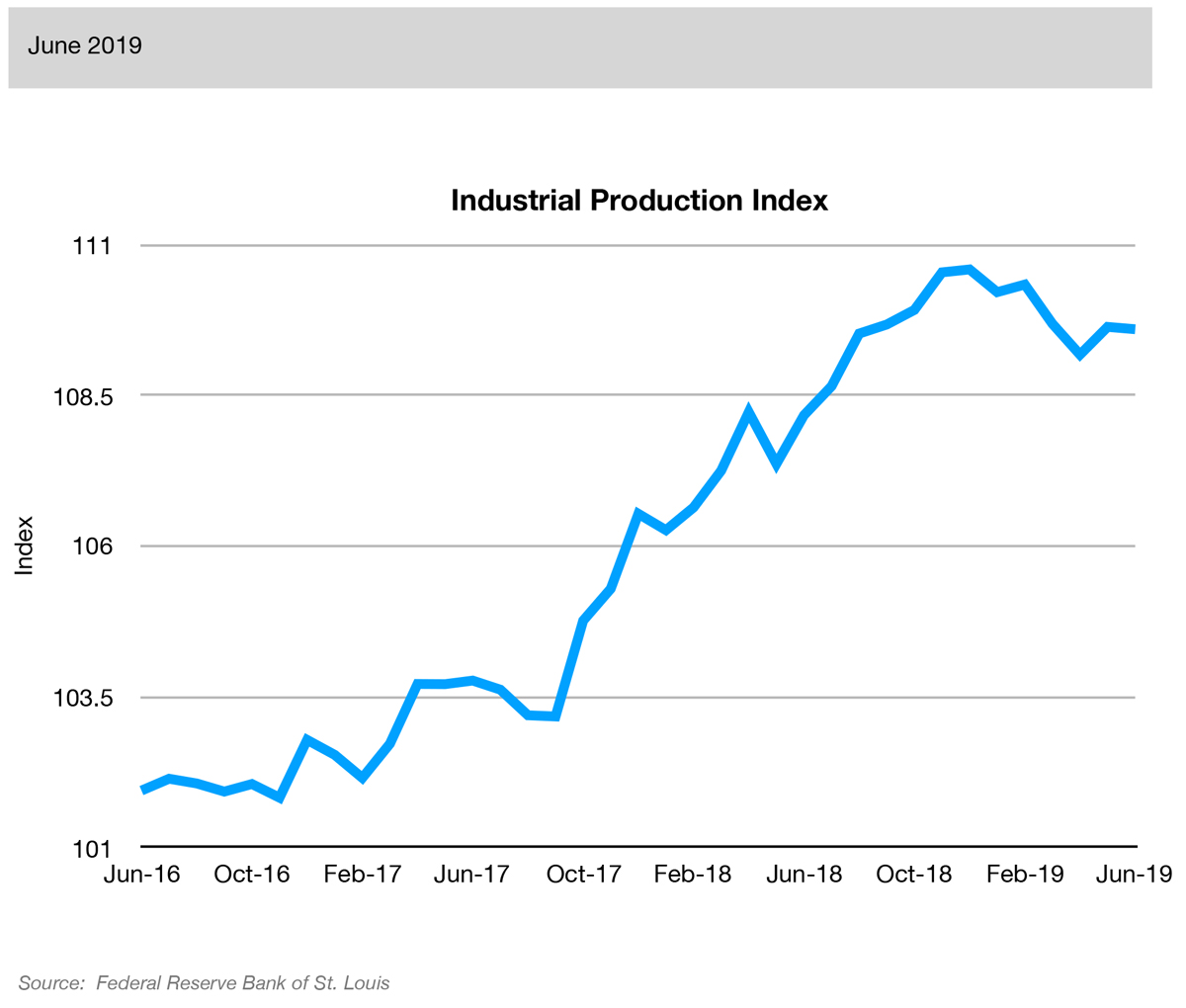
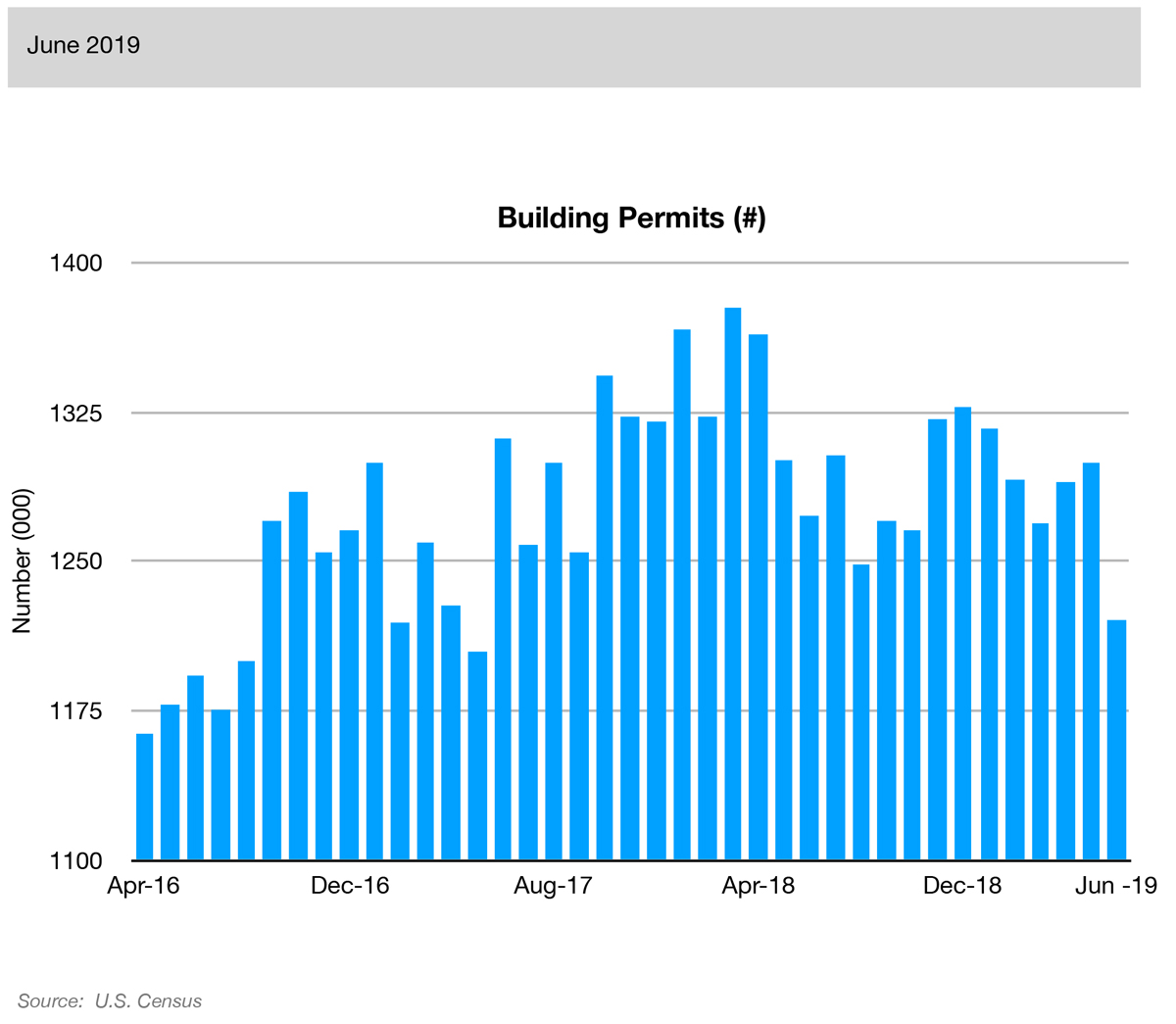
On the other hand, businesses are slowing down; the Industrial Production Index declined at -0.1%. Furthermore, they continue to reduce orders and investments: the ISM Manufacturing Index posting -6.5% and Building Permits measuring -5.3%. These numbers suggest that companies are not in an expansionary mood and that manufacturing and housing are entering difficult times.
There is a clear divergence between consumer spending and a slowdown in business activity, a condition that is not sustainable and eventually will have to converge. Furthermore, by the end of June, the yield on the U.S. 10-year Treasury note dipped below the return on the 3-month paper, i.e., 2.00% vs. 2.12%. This condition is not normal and is considered a predictor of a recession within a year.
On a broader note, businesses have been enduring trade tariffs for two years – not an insurmountable obstacle in itself as firms can adjust prices. However, the continued tension between the U.S. and China is suggesting a more significant split and, ultimately, a deeper economic slowdown.
EXHIBIT 1. A DASHBOARD OF THE U.S. ECONOMY
Lagging Indicators
Change
GDP Growth measures how fast the economy is growing. It does this by comparing one quarter of the country’s domestic product to the previous quarter. It is driven by four components: personal consumption, business investment, government spending, and net trade. GDP Growth is the most important indicator of the health of the economy. It changes during the four phases of the business cycle: peak, contraction, trough, and expansion.
Source: InvestopediaThis index measures the amount of output from the manufacturing, mining, electric, and gas industries. The reference year for the index is 2002 and a level of 100. A measure growing month-over-month is a sign that the companies in the industry are performing well.
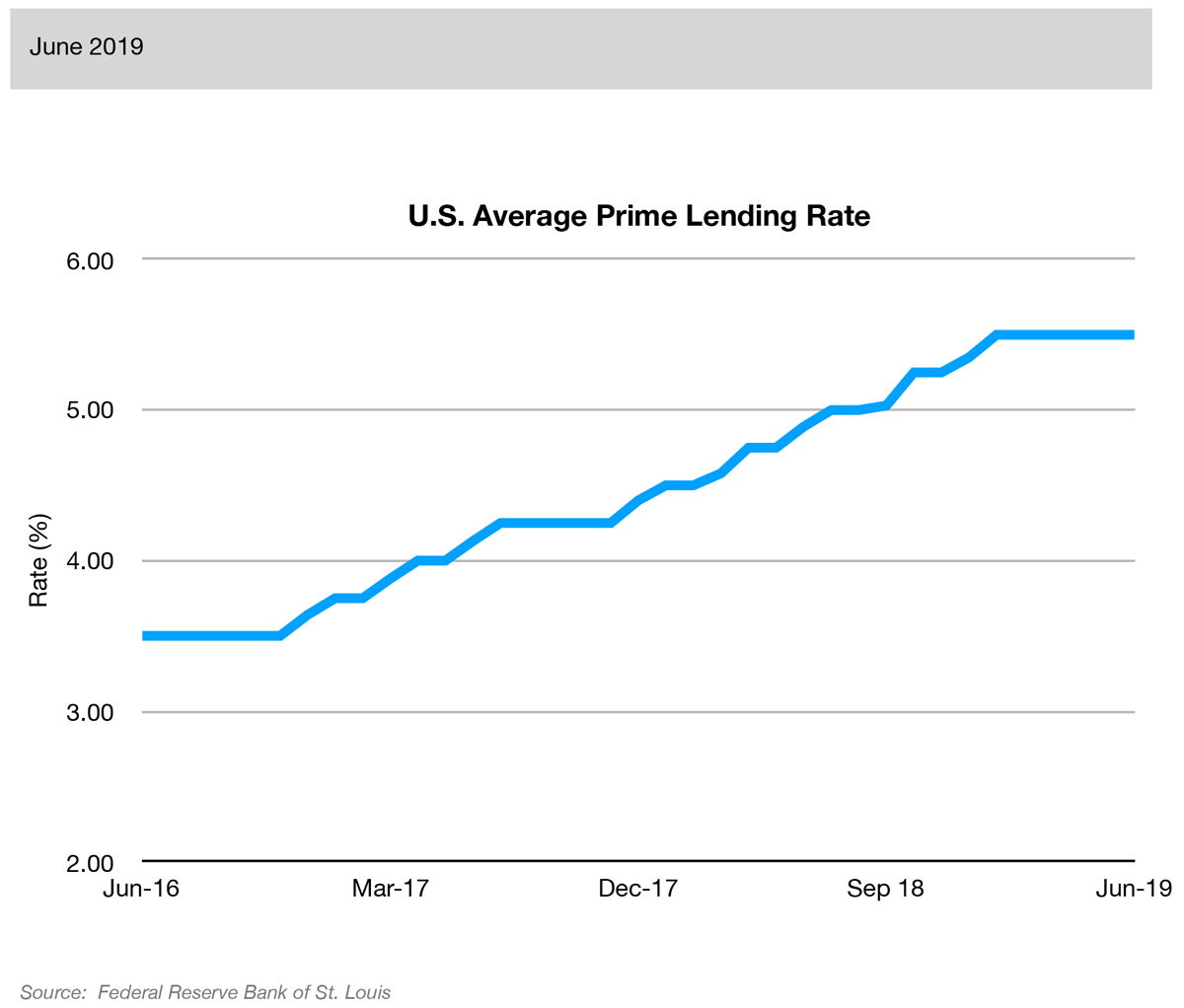
Source: InvestopediaThis measure is the average rate of interest charged on short-term loans by commercial banks to companies. High interest rates discourage businesses to borrow and invest. As a result, GDP growth slows down. Low rates can lead to an increased demand for money and raise the likelihood of inflation.
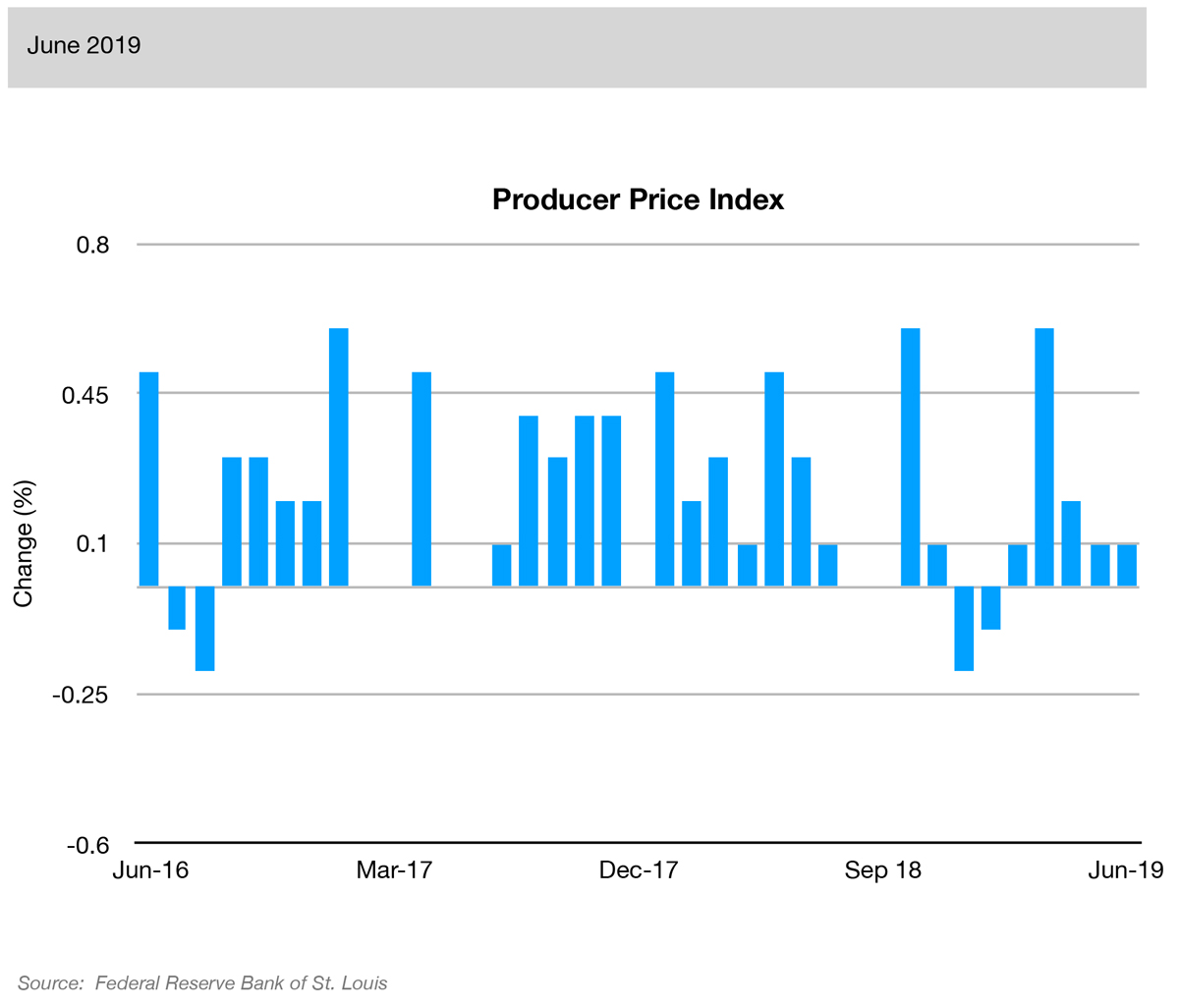
Source: WT Wealth ManagementThis index measures the average change over time in the selling prices received by domestic producers for their output, including finished goods, intermediate goods and crude goods. The index is timely because it is the first inflation measure available in the month.
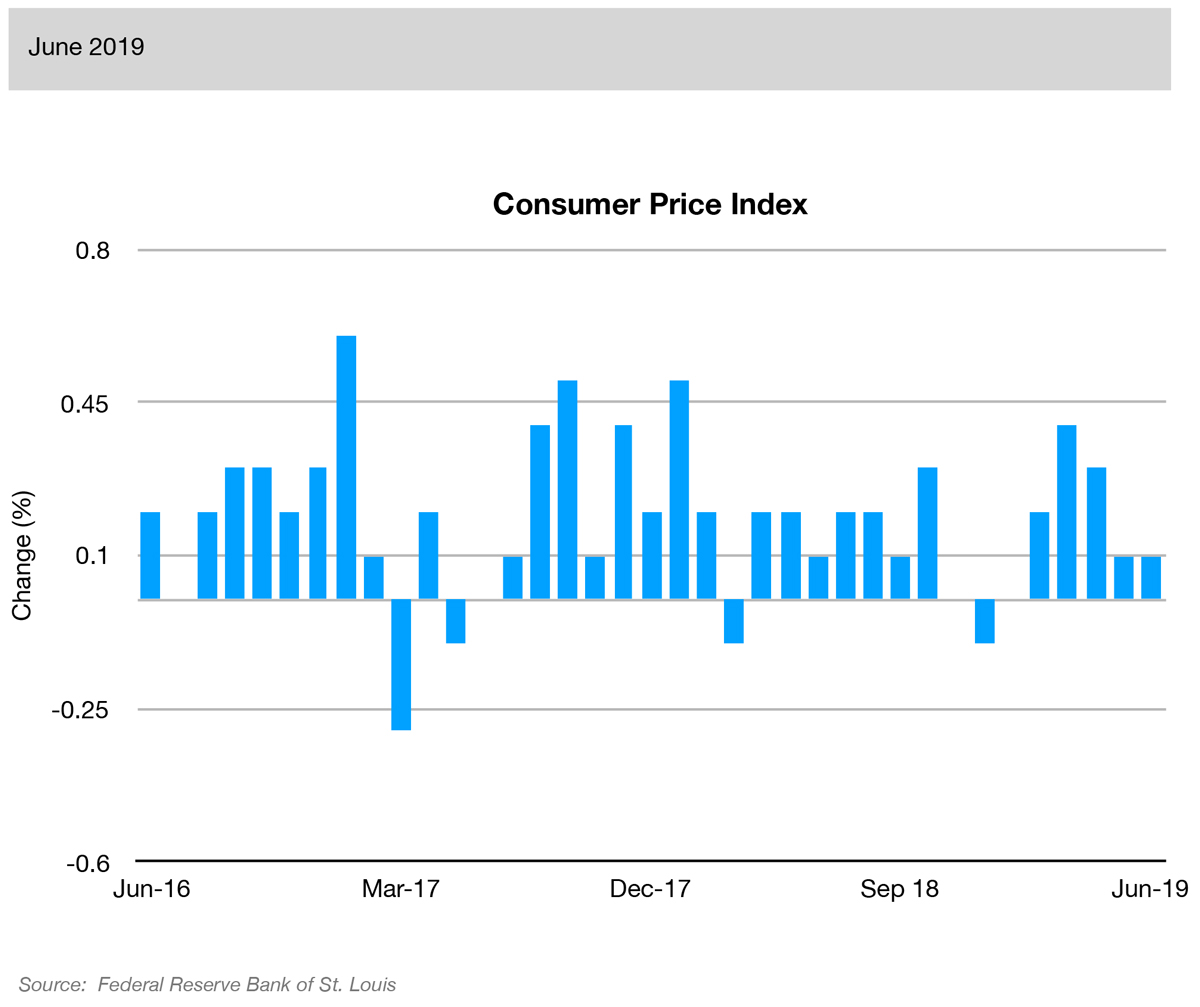
Source: American Association of Individual InvestorsThis index reflects monthly data on changes in the cost of living, or inflation. A high rate of inflation may erode the value of the dollar more quickly than the average consumer’s income can compensate, thus decrease consumer purchasing power. The index is the best indicator of inflation.
Source: American Association of Individual InvestorsLagging indicators depict current economic conditions and confirm turning points in the economy.
Leading Indicators
Change
Historically, readings of 50 percent or above are associated with an expanding manufacturing sector and healthy GDP growth overall. Readings below 50 indicate a contracting manufacturing sector but overall GDP growth is still positive until the ISM index falls below 42.5 (based on statistics through January 2011).
Source: Bloomberg News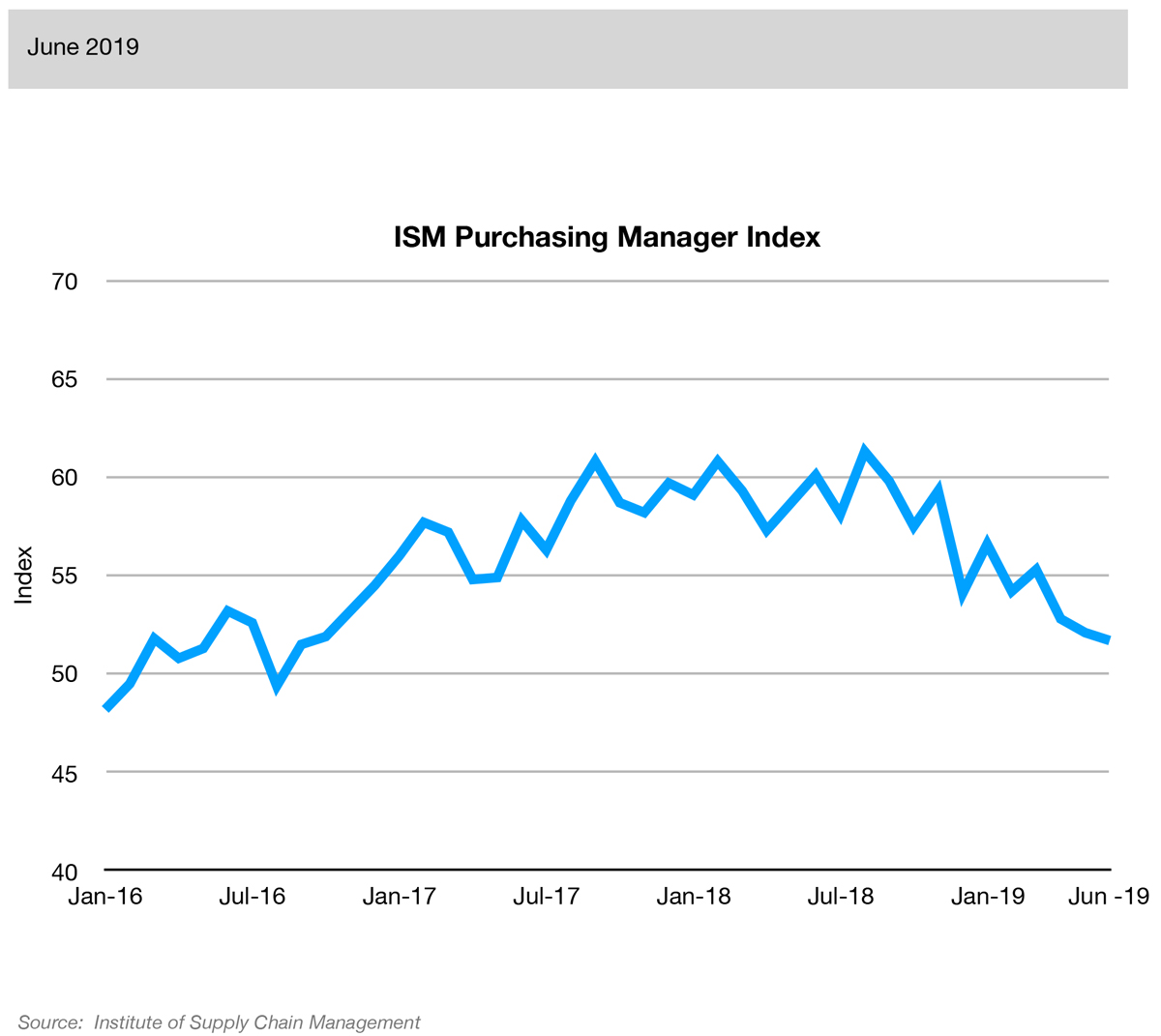
The housing construction market is one of the first economic sectors to rise or fall when economic conditions improve or degrade, and building permits can be an early indicator of activity in the housing construction market.
Strong retail sales directly increase GDP. When sales improve, companies can hire more employees to sell and manufacture more product, which in turn puts more money back in the pockets of consumers. Weak retail sales have the opposite effect.
Source: WT Wealth Management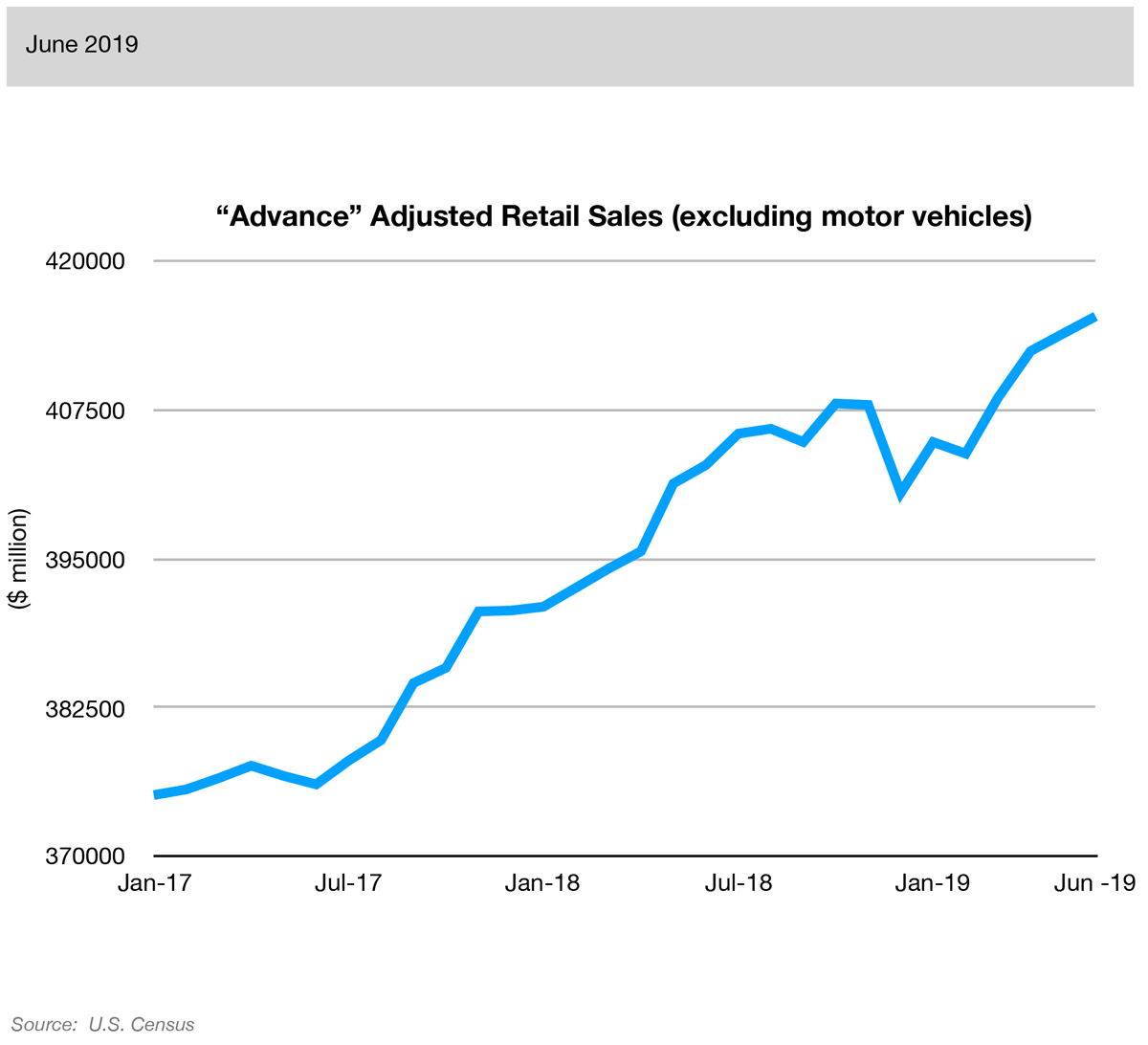
The index measures overall consumer sentiments about business toward the short-term (12-month) future economic situation.
The index is used as a gauge of future business and consumer confidence levels. Growth of the S&P 500 index can translate into growth of business investment. It can also be a clue to higher future consumer spending. A declining index can signal a tightening of belts for both businesses and consumers.
Source: American Association of Individual Investors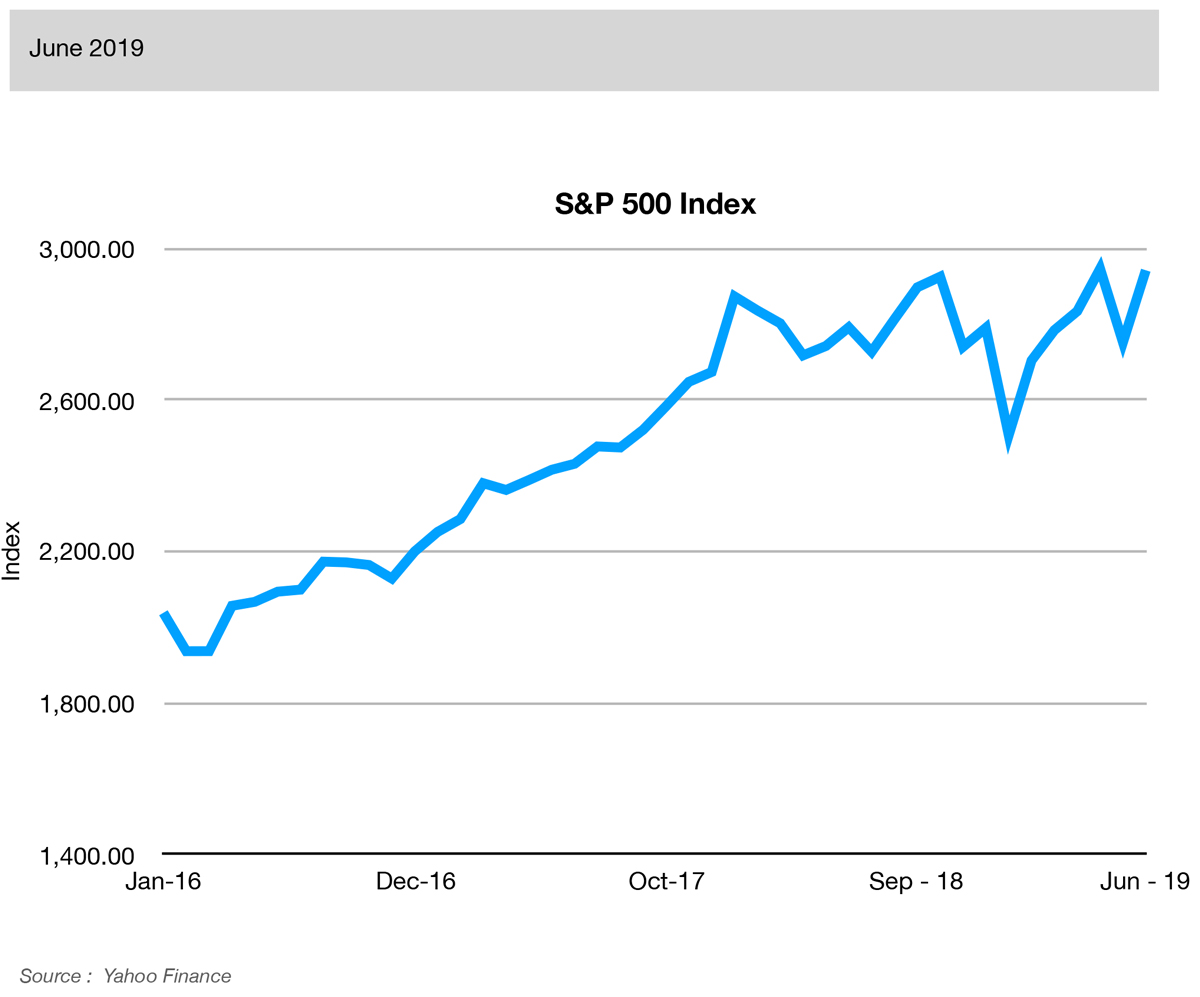
Leading indicators are first to change direction ahead of a business cycle and signal change before actual changes occur in the economy.
On display, a dashboard of select economic indicators appropriate for business managers helps to take a meaningful snapshot of the economy. Any single indicator taken in isolation provides little value. Together at the dashboard level, the indicators and their supporting charts offer a current high-level view and an easy comparison to draw your conclusions about the economic outlook, changes in the economic cycle, or other critical economic shifts.
How will the current economic
outlook impact your business?
PREPARING FOR A SLOWDOWN
As the slowdown takes effect, important realities set in. The industry inevitably shifts, revenue growth slows down, and as your company’s competitive position comes into greater focus, its vulnerabilities become more explicit. The net effect is that as the firm becomes more exposed to economic headwinds, it also becomes more vulnerable to the competition.
While a slowdown is not a crisis, management needs to plan ahead if it continues. The way out of this situation is to get ahead of the slowdown and move first, before competitors.
TAKING PROACTIVE ACTION
Proactive firms plan ahead of slowdowns – when things are going well – and take action early. This strategy allows them to act deliberately, instead of reacting to circumstances. By so doing, they get ahead of the slowdown and, most importantly, they get ahead of the competition.
They recognize the need to balance cutting cost in the short-term without having to sacrifice growth in the long term. Here are the steps you can take:
Reduce Costs and Manage Cash Tightly. Take a strategic approach to cost-cutting and capital preservation to withstand the slowdown while preserving capital for growth initiatives. Because businesses can quickly become cash strapped, manage cash tightly, streamline inventory, and reduce accounts receivables – a strong balance sheet positions the company to fund capabilities for long-term growth.
Defend Your Market Position. As part of the regular course of business, new threats emerge all the time as challengers try to take a piece of the action. Attacks become all the more prominent during a slowdown. Even if the firm is in a strong defensive position with stable cash flows, it can become exposed to new threats and new vulnerabilities. For these reasons, monitoring and defending are vital to the well-being and the existence of the firm.
Pursue Long Term Profitable Growth. In dealing with a slowdown, it’s all too common for managers to focus their attention exclusively on cost cutting. However, the biggest gains during slowdowns result from revenue growth. This realization means investing in critical capabilities for future growth and taking advantage of shifting markets and M&A opportunities that struggling competitors cannot pursue.
CONCLUSION
During an economic slowdown, the context is similar for every company. The critical point is to get ready and perform better than competitors. There is a finite amount of time and a limited number of levers to use. The strategy is to move quickly ahead of the pack and take the right steps on three fronts: cost management, market defense, and profitable growth.
What is your next move?