Market forces affect the equilibrium between supply and demand all the time. For instance, a typical situation of rising production costs drives excess capacity in the market and a shift in the supply curve. Another scenario of a drop in market demand causes a reduction in the equilibrium price and quantity of that good. In both cases, supply will exceed demand, a condition that can exert considerable pressure on profit margins and, in some case, drive companies out of the market. What can managers do?
WHAT DOES THE INDUSTRY COST CURVE LOOK LIKE?
Business managers should rely on the industry cost curve to guide their actions. This object of analysis is fundamental to making informed decisions on cost, production capacity, pricing, and competitive initiatives.
The industry cost curve plots available production capacity by competitor against unit cost (Exhibit 1). Unit cost comprises all costs of the delivered product. These include direct costs of labor, materials, and subcontracting, as well as indirect costs such as administration, marketing, sales, depreciation of inventory, buildings and equipment, indirect labor, maintenance, warehousing, transportation, and more.
Exhibit 1. The Industry Cost Curve
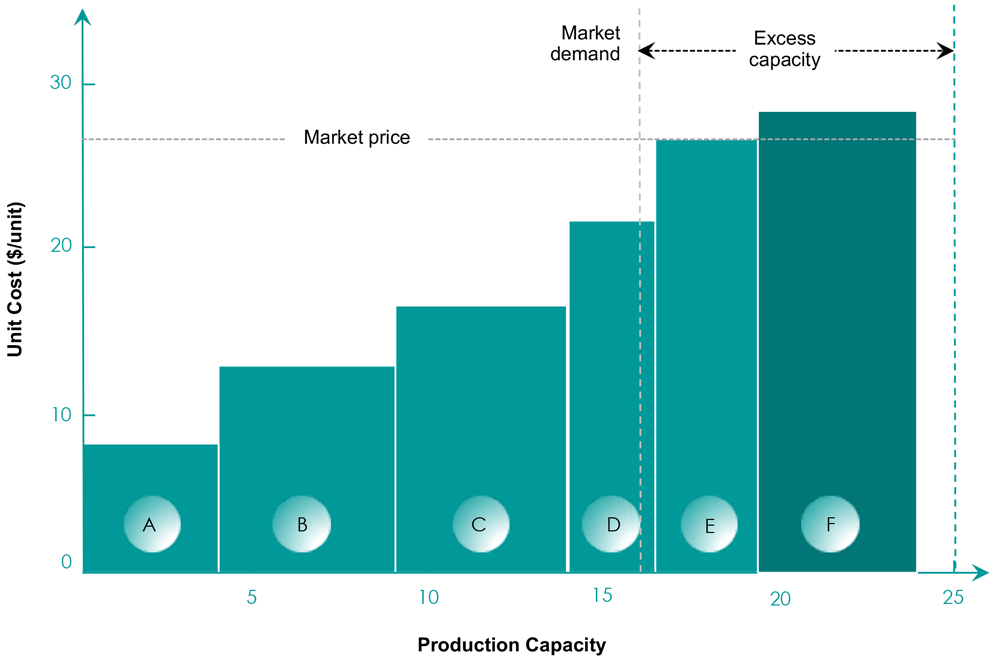
Importantly, the industry cost curve provides a full picture of the cost situation and the production capacity in the industry. It serves to compare the company’s cost position directly against its direct competitors, i.e., its relative cost position. This knowledge is fundamental in determining where the company stands, the extent of its competitiveness in an oversupplied market, and the level of improvement it might need to achieve to remain competitive. Typical strategic issues that arise in this context include the following:
- How should companies E and F deal with elevated cost and excess capacity?
- What if the cost curves differ from one market to another while capacity constraints are limiting the total available volume?
- Should company D seek to undercut its price to improve its utilization ratio?
- Should companies A, B, or C attempt to consolidate the market to retire industry capacity?
These are essential considerations that require intimate knowledge of the market, cost, and competitors.
ADDRESSING THE PROBLEM
The problem of an oversupplied market unfolds gradually, is challenging to detect, and complex to resolve. By the time it becomes visible, it is usually well underway. This condition is systemic as it affects all companies in the market, albeit to a different extent. Nevertheless, management needs to address the situation sooner than later because it only gets worse over time. Critical considerations to guide management include the following:
- What is our position in terms of cost and production capacity?
- How do we compare to our direct competitors?
- What is our source of cost advantage/disadvantage?
- What target cost structure do we need to achieve to stay competitive?
- What level of capacity utilization do we need to target?
- What actions do we need to put in place?
- Will the positive outcomes of these actions be sufficient to address the problem?
- If not, what other measures should we plan on taking?
The proper response to an oversupplied market requires strategic action. Executives need to push beyond conventional cost tactics and consider focusing on the larger picture to achieve the optimal level of cost and production capacity for their company.

